An introduction to the Knewton API

In this section:
The Knewton API exposes constructs designed to support a variety of learning applications spanning a range of educational use cases. To integrate with Knewton, the application designer must understand the features that the Knewton API provides, identify the subset of features their application must rely upon, and connect the application’s logic to corresponding API endpoints.
This page outlines the key abstractions and organizing principles of the Knewton API, contextualizing the other pages of this Implementation Guide, which offer more in-depth coverage of the API features.
The primary purpose of the Knewton API is to provide learning applications with useful analytics and recommendations to power adaptive learning experiences and provide actionable insights to students and instructors. Before these benefits can be realized, the Knewton Platform must first be made aware of the learning application’s users and seeded with information about the pedagocial intent and learning objectives of any adaptive assignments that students will be asked to complete, about the interactions of students with content items, and about the content itself.
To that end, a partner application must create and manage the following types of entities defined by the Knewton Platform data model.
The relationships between these entities are shown in the figure below.
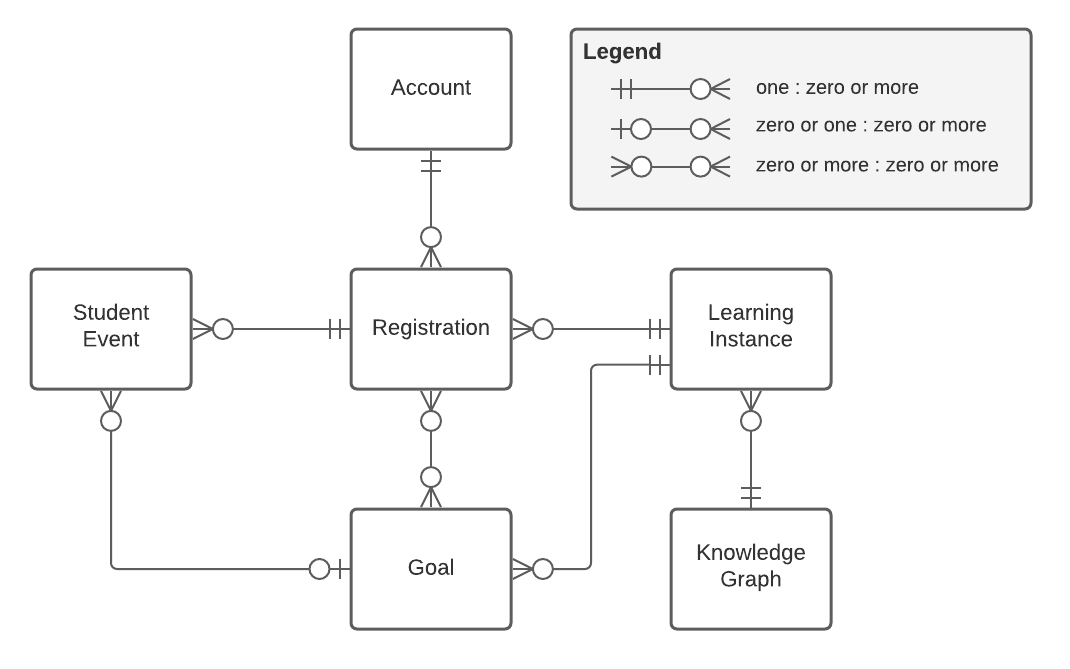
The entities described in the Knewton Platform’s Data Model must be sent to the Knewton Platform, via offline processes in some cases and via the Knewton API in other cases, before meaningful recommendations or analytics can be retrieved.
The figure below shows the dependencies between the provisioning operations for the different types of entities.
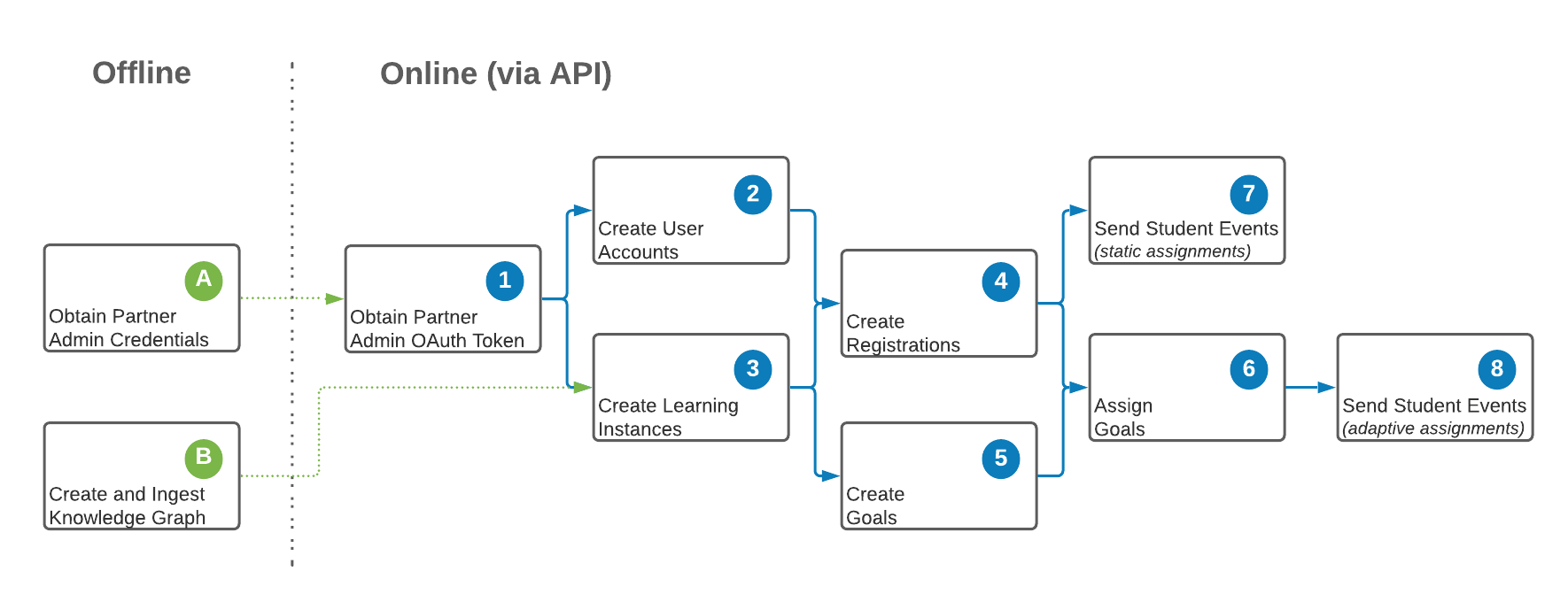
All of these provisioning operations are typically performed on an ongoing basis as new users, courses/learning contexts, enrollments, assignments, and student interactions are recorded by the learning application, or as previously created entities are updated.
The Knewton Platform creates UUID identifiers for any resources created through the Knewton API. In many cases this ID will need to be included in subsequent API requests that reference previously created entities.
For example, the request payload to create a Registration resource must contain the Knewton-provided UUIDs for the Account and the Learning Instance that the Registration associates. To register a user with a corresponding Knewton Account ID 3de63120-ebcd-4568-935a-0d04e3bf0f72 into a course with a corresponding Knewton Learning Instance ID 41409a38-3153-41f8-aa90-d6bacb7e23ed, the learning application would create a resource under
/registrations:
POST /v0/registrations
{
"account_id": "3de63120-ebcd-4568-935a-0d04e3bf0f72",
"learning_instance_id": "41409a38-3153-41f8-aa90-d6bacb7e23ed",
"type": "learner"
}
The Knewton Platform creates the registration, assigns it its own ID, and returns that ID in the response.
{
"id": "83ce46e1-ae1e-493a-95ab-826ee02a4118",
"account_id": "3de63120-ebcd-4568-935a-0d04e3bf0f72",
"learning_instance_id": "41409a38-3153-41f8-aa90-d6bacb7e23ed",
"type": "learner"
}
Whenever a Knewton API response includes the ID of a created resource, the learning application is expected to store that ID and associate it with whatever entity in the learning application’s data model corresponds to the created Knewton Platform resource so that it can be looked up and used as needed in subsequent requests.
POST /v0/accounts.POST /v0/learning-instances/.POST /v0/registrations/.POST /v0/learning-instances/{li_id}/scoped-goals.GET /v0/registrations/{registration-id}/recommendation. (Note that this is a slightly different case, in that the Recommendation resource is created automatically by the Knewton Platform and mererly retrieved by the learning application.)Now the fun part! Once the learning application has implemented the required provisioning flows, the Knewton Platform will start to build up an understanding of students’ mastery of the different concepts defined in the Knowledge Graph, and the learning application can retrieve recommendations and analytics. See the following sections of this implementation guide for more ideas about how to use these capabilities to build awesome features that your users will love!
Getting Started
Working with Adaptive Assignments
Predictive Learner Analytics
General API Usage
Brand Guidelines
Glossary